What is Graphene Oxide?
Graphene is a material made of carbon atoms that are bonded together in a repeating pattern of hexagons. Graphene is so thin that it is considered two dimensional. Graphene is considered to be the strongest material in the world, as well as one of the most conductive to electricity and heat. Graphene has endless potential applications, in almost every industry (like electronics, medicine, aviation and much more).
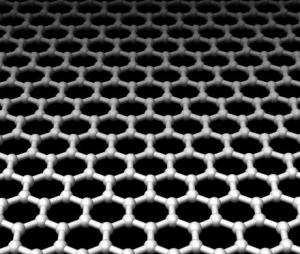
As graphene is expensive and relatively hard to produce, great efforts are made to find effective yet inexpensive ways to make and use graphene derivatives or related materials. Graphene oxide (GO) is one of those materials - it is a single-atomic layered material, made by the powerful oxidation of graphite, which is cheap and abundant. Graphene oxide is an oxidized form of graphene, laced with oxygen-containing groups. It is considered easy to process since it is dispersible in water (and other solvents), and it can even be used to make graphene. Graphene oxide is not a good conductor, but processes exist to augment its properties. It is commonly sold in powder form, dispersed, or as a coating on substrates.
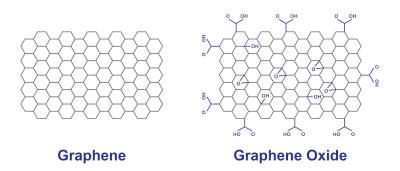
Graphene oxide is synthesized using four basic methods: Staudenmaier, Hofmann, Brodie and Hummers. Many variations of these methods exist, with improvements constantly being explored to achieve better results and cheaper processes. The effectiveness of an oxidation process is often evaluated by the carbon/oxygen ratios of the graphene oxide.
Graphene oxide uses
Graphene Oxide films can be deposited on essentially any substrate, and later converted into a conductor. This is why GO is especially fit for use in the production of transparent conductive films, like the ones used for flexible electronics, solar cells, chemical sensors and more. GO is even studied as a tin-oxide (ITO) replacement in batteries and touch screens.
Graphene Oxide has a high surface area, and so it can be fit for use as electrode material for batteries, capacitors and solar cells. Graphene Oxide is cheaper and easier to manufacture than graphene, and so may enter mass production and use sooner.
GO can easily be mixed with different polymers and other materials, and enhance properties of composite materials like tensile strength, elasticity, conductivity and more. In solid form, Graphene Oxide flakes attach one to another to form thin and stable flat structures that can be folded, wrinkled, and stretched. Such Graphene Oxide structures can be used for applications like hydrogen storage, ion conductors and nanofiltration membranes.
Graphene oxide is fluorescent, which makes it especially appropriate for various medical applications. bio-sensing and disease detection, drug-carriers and antibacterial materials are just some of the possibilities GO holds for the biomedical field.
Buy Graphene Oxide
Graphene oxide is relatively affordable and easy to find, with many companies that sell it. It does, however, get confusing since different companies offer products that vary in quality, price, form and more - making the choice of a specific product challenging. If you are interested in buying GO, contact Graphene-Info for advisement on the right GO for your exact needs!
Further reading
The latest graphene oxide news:
A new version of our Graphene Oxide Market report released
Today we published a new edition of our Graphene Oxide Market Report, with all the latest information, including both new research activities and updates from companies. Our market report is a comprehensive guide to graphene oxide (and r-GO) materials and their promising applications in energy storage, composite materials, bio-medical, water treatment and more.
Reading this report, you'll learn all about:
- The difference between graphene oxide and graphene
- Graphene oxide properties
- Possible applications for graphene oxide
- Reduction of graphene oxide to r-GO
The report package also provides:
- A list of prominent GO research activities
- A list of all graphene oxide developers and their products
- Datasheets for over 20 different GO materials
- Free updates for a year
This Graphene Oxide market report provides a great introduction to graphene oxide materials and applications, and covers everything you need to know about GO materials on the market. This is a great guide for anyone interested in applying graphene oxide in their products.
Researchers use green chemistry approach to synthesize graphene oxide/silver nanocomposites
Researchers from Pakistan have reported a green approach to the synthesis of graphene oxide/silver nanoparticle nanocomposite.
Metallic nanoparticles (NPs) have various benefits in the field of electrochemistry. Because of their small size, nanoparticles may enhance the contact area of the electrode in use. Furthermore, metallic nanoparticles may boost the rate of mass transfer and provide quick electron transference, increasing the sensitivities of the used electrodes. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are relatively low cost and have distinct physical and chemical characteristics that make them helpful in several optical, chemical, and catalytic functions. Nanoscale composites of metallic nanoparticles and graphene oxide have promising applications in energy storage, supercapacitors, and electronics.
William Blythe expands its graphene oxide capacity to 50 tonnes as demand increases
UK-based graphene Oxide developer William Blythe announced that as the company enjoys increasing demand for its graphene materials, it has scaled up its production from lab-scale to 50-tonne capacity.

William Blythe started to develop its graphene technologies in 2016, and started to supply small quantities of the material in 2016. The company since has been working with world-leading organizations to advance its technology and applications research.
G6 Materials launches Breathe+ Pro Advanced Antimicrobial Graphene Air Filtration System
G6 Materials Corporation has announced the launch and immediate availability of the Breathe+ Pro Advanced Antimicrobial Graphene Air Filtration System.

The Breathe+ Pro Advanced Antimicrobial Graphene Air Filtration System removes microbes, dust particles, smog, dander, pollen as well as volatile organic compounds (VOC) from the air. Its antiviral and antibacterial efficacy was reportedly verified by independent tests by The Intertek Group. This patented Graphene Filter is said to remove 99.9% of the pathogenic microorganisms and is optimized for spaces up to 1,500 sq. ft., making it suitable for the home and office.
Graphmatech, Graphenea, and Northvolt produce graphene oxide from recycled EV batteries
Graphmatech, Graphenea, and Northvolt have announced their success in up-cycling end-of-life EV batteries into graphene oxide at industrial pilot scale. This breakthrough uses the material left after Northvolt has extracted valuable metals and minerals. Until now, that remaining material was left as waste.
Emma Nehrenheim, Chief Environmental Officer of Northvolt, comments: The upcycling of graphene oxide from recycled batteries represents a great development in our pursuit of a sustainable battery industry in Europe. Batteries contain an abundance of valuable materials which we can recover to reduce our dependence on mining and producing fresh materials. We are proud to have contributed to this development.
China-based researchers design new method to pre-enrich uranium in seawater using graphene oxide
Researchers at the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with teams from China's Lanzhou University and Hebei University, have developed a graphene oxide-based method of pre-enriching uranium in seawater by membrane filtration.
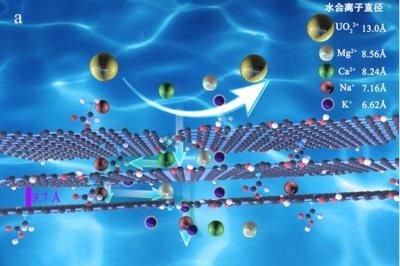
In their study, the scientists fabricated a new type of glycine cross-linked composite graphene oxide (GO-Gly) membrane with good ion sieving properties, which can meet the demands of uranium pre-enrichment in seawater.
Graphene oxide helps use disposable face masks to make better concrete
A Washington State University (WSU) research team recently showed that used single-use masks, of the kind made ubiquitous in the pandemic, can be incorporated into a cement mixture (with the help of graphene oxide) to create stronger, more durable concrete. The team found that the mixture using mask materials was 47% stronger than commonly used cement after a month of curing.

These waste masks actually could be a valuable commodity if you process them properly, said Xianming Shi, professor and interim chair of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and the corresponding author on the paper. I’m always looking out for waste streams, and my first reaction is ‘how do I turn that into something usable in concrete or asphalt?’
Graphene-Info updates all its graphene market report
Today we published new versions of all our graphene market reports. Graphene-Info provides comprehensive niche graphene market reports, and our reports cover everything you need to know about these niche markets. The reports are now updated to April 2022.
The Graphene Batteries Market Report:
- The advantages using graphene batteries
- The different ways graphene can be used in batteries
- Various types of graphene materials
- What's on the market today
- Detailed specifications of some graphene-enhanced anode material
- Personal contact details into most graphene developers
The report package provides a good introduction to the graphene battery - present and future. It includes a list of all graphene companies involved with batteries and gives detailed specifications of some graphene-enhanced anode materials and contact details into most graphene developers. Read more here!
Researchers shed light on the behavior of graphene oxide at extreme temperatures
Researchers from Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, Joint Institute for High Temperatures of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology, Saint Petersburg State Marine Technical University, Institute of Nanotechnology of Microelectronics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Bauman Moscow State Technical University and Emanuel Institute of Biochemical Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences have found the reason why instead of burning down at high temperatures, graphene oxide opens the door to a promising and inexpensive graphene production method.
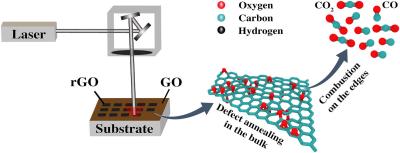
The search for a cheap and efficient route of graphene fabrication is still ongoing. Graphene reduction from graphene oxide by laser irradiation appears as a promising route: with graphene oxide produced from ordinary graphite using chemical methods, the laser-aided reduction technique holds much promise in terms of cost and controllability of the resulting material quality.
Researchers develop a graphene oxide aerogel foam to improve all solid state lithium batteries
Researchers from China's Jiangsu University and Changzhou University have developed a non-ceramic solid-state electrolyte based on a graphene oxide (GO) aerogel framework filled with polyethylene oxide.
Li-ion batteries currently perform a key role in electric cars, but contain combustible liquid electrolytic materials which may pose major safety issues. The solid-state electrolyte (SSE) can replace the standard organic liquid electrolyte and is predicted to address safety issues such as leaking, heat runaway, and even explosions during operation.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 4
- Next page


