Researchers from Nanotek Instruments have developed a new graphene-based supercapacitor that can store as much energy as NiMH batteries, but charge and discharge in minutes or even seconds. The new device has a specific energy density of 85.6 Wh/kg at room temperature and 136 Wh/kg at 80 °C. These are the highest ever values for "electric double layer" supercapacitors based on carbon nanomaterials.
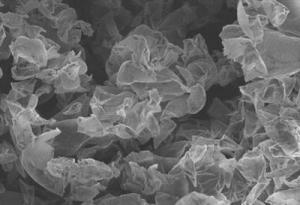 Curved graphene sheets
Curved graphene sheets
The new supercapcitor has electrodes made of graphene mixed with 5wt% Super P (an acetylene black that acts as a conductive additive) and 10wt% PTFE binder. A sheet of carbon just one atom thick, graphene is a very good electrical conductor as well as being extremely strong and flexible.
The problem with single-layer Graphene sheets, according to the team, is that they tend to re-stack together. They are trying to overcome this problem by developing a strategy that prevents the graphene sheets from sticking to each other face-to-face. This can be achieved if curved graphene sheets are used instead of flat ones.