In 2013, Rice University researchers developed a simple method to reduce coal into graphene quantum dots (GQDs). Now the researchers combined these GQDs with small graphene oxide (GO) sheets to create an excellent catalyst for fuel-cells.
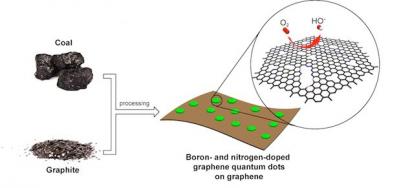
To create the new materials, the researchers boiled a solution of GQDs and GO sheets - which combined them into self-assembling platelets. Treating those platelets with nitrogen and boron created a material with an abundance of edges for chemical reactions (for oxygen reduction), and excellent conductivity.
The new material features an oxygen reduction reaction of about 15 millivolts and a current density 70% larger than platinum-based catalysts. The new material should be cheaper than platinum-based catalysts.

