Scientists from Princeton, the University of Leeds, the University of California and the National Institute for Material Science in Japan have used innovative techniques to visualize electrons in graphene, and found that strong interactions between electrons in high magnetic fields drive them to form unusual crystal-like structures similar to those first recognized for benzene molecules in the 1860s by chemist August Kekulé.
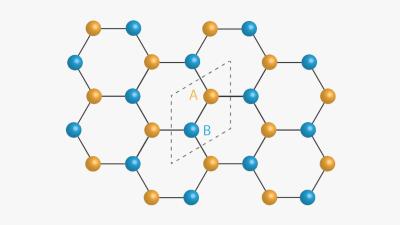
These crystals exhibit a spatial periodicity that corresponds to electrons being in a quantum superposition. The experiments also showed the Kekulé quantum crystals have defects that have no analog to those of ordinary crystals made up of atoms. These findings shed light on the complex quantum phases electrons can form because of their interaction, which underlies a wide range of phenomena in many materials.
Previous studies have shown that graphene demonstrates novel electrical properties, Yazdani said. But never before have researchers been able to peer so deeply and with such spatial resolution into the nature of quantum states.
To achieve this level of resolution, Yazdani’s group used a scanning tunneling microscope (STM). This device relies on a phenomenon called quantum tunneling, where voltage is used to funnel electrons between the sharp metallic tip of the microscope and the sample only a few Ã¥ngströms away. The microscope uses this tunneling current rather than light to view the world of electrons on the atomic scale. Yazdani’s microscopes operate in a very high vacuum to keep the sample surface clean and at very low temperatures to allow for high resolution measurements, unperturbed by thermal agitation.
The microscope is also able to view electrons as they reach their lowest energy states dominated by their quantum properties.
In the presence of a magnetic field, the microscope can be used to determine the spatial structure of the quantized energy level.
One of the special properties of graphene is its behavior in a magnetic field, when electrons are forced to orbit around the magnetic field in a circle, said Yazdani. This quantizes their energies, resulting in quantization of graphene’s electrical properties.
Quantization of energy refers to the creation of discrete values of energy, without any intermediate values, which is a characteristic of quantum physics, as opposed to classical physics, where continuous energy values is permitted.
The researchers focused their attention on the quantized level with the lowest energy in graphene, for which previous research first reported by Phuan Ong, Eugene Higgins Professor of Physics at Princeton, had revealed some unusual electrical properties. This level dominates the electrical properties when there are no excess charges added or removed from graphene â in other words, when the charge is neutral. Ong had shown that electrons freeze when the charge is neutral, and the graphene layer acts as an insulator with the application of a magnetic field. The nature of this frozen state of electrons in graphene has been a mystery for almost a decade, since Ong’s initial discovery.
The insulating state that we found puzzled everyone and strongly challenged the prevailing theories at that time, said Ong, who was not involved in the current research. It remained an enduring puzzle for 13 years until the beautiful results obtained by Yazdani. The new results resolve the puzzle in a very exciting fashion.
Yazdani and his team used the microscope to map the wavefunction of the lowest quantized energy level in the presence of a magnetic field. The researchers found complex patterns of electron waves when graphene was tuned to a neutral state with a nearby electrical gate.
In metals, electrons’ wavefunction are spread throughout the crystal, while in a normal insulator, electrons are frozen without any particular preference to the crystal structure of the atomic sites. At very low fields, STM images showed electron wavefunctions of graphene choosing one of the sub-lattice sites over the other. More importantly, by increasing the magnetic field, a remarkable bond-like pattern is observed, which corresponds to electrons’ wavefunction residing in a quantum superposition. This means that an electron occupies the two inequivalent sites at the same time.
In particular, the image corresponded to the bond-like structure first recognized by Kekulé for benzene. This consists of alternating single and double bonds. In a single bond, one electron from each atom binds with its neighbor electron; in a double bond, two electrons from each atom participate.
People have speculated that electrons may form such Kekulé patterns, said Yazdani, but now we’re seeing it for the first time. One couldn’t distinguish this state of electrons any other way unless it is imaged.
The researchers then used the microscope to map the uniformity of the Kekulé crystal and its properties near imperfections, or defects in the graphene. One remarkable finding they made was near charge defects where they found the Kekulé pattern to evolve continuously in its patterns around the defect on the graphene surface.
Teaming up with Michael Zaletel of the University of California, Berkeley, the team developed a method for extracting from the STM data the mathematical properties of the quantum wavefunction of electrons, so-called phase angles describing their quantum superposition. The analysis revealed remarkable winding of one of these phase angles around the defect and correlated changes in the other angle.
"When the group applied their technique to measure the phase-angle above a defect in the substrate, they found a ‘vortex’ in the Kekulé pattern, which is like a hurricane around which the phase-angle winds around by 12 hours [as on a clock], said Zaletel. When making predictions about such quantum, nanoscale, objects, you rarely think you’ll have the pleasure to really ‘see’ a picture of them, but the group has been able to do just that."
The team believes that the techniques they have developed to uncover this unusual quantum crystal of electrons in a strong magnetic field can have applications elsewhere in the field. Other two-dimensional materials and their stack can exhibit similar quantum crystals with novel defects. The team aims to apply their methodology to a wider class of such materials.
In addition to Yazdani and Zaletel, contributors to the study included authors Xiaomeng Liu, Gelareh Farahi and Cheng-Li Chiu, all at the Joseph Henry Laboratories and Department of Physics, Princeton University; Zlatko Papic, School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leeds, United Kingdom; and Kenji Watanabe and Takashi Taniguchi of the National Institute for Material Science in Japan.
The study, Visualizing broken symmetry and topological defects in a quantum Hall ferromagnet, by Xiaomeng Liu, Gelareh Farahi, Cheng-Li Chiu, Zlatko Papic, Kenji Watanabe, Takashi Taniguchi, Michael Zaletel and Ali Yazdani, was published Dec. 2, 2021 in the journal Science (DOI: 10.1126/science.abm3770).
This work was primarily supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF-DMR-1904442 and ONR-N00014-21-1-2592). Other major support came from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation’s EPiQS initiative grant (GBMF9469, NSF-MRSEC) through the Princeton Center for Complex Materials (NSF-DMR-2011750, DOE-BES grant DE-FG02-07ER46419), the Princeton Catalysis Initiative; the Elemental Strategy Initiative, Japan (JPMXP0112101001, JSPS KAKENHI grant JP20H00354, CREST JPMJCR15F3, JST to K.W. and T.T.); and the Army Research Office through the MURI program (W911NF-17-1-0323 to M.P.Z.). The researchers also acknowledged the hospitality of the Aspen Center for Physics (supported by NSF grant PHY-1607611), Trinity College (supported by a QuantEmX grant from ICAM), and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation (GBMF9616).



