Researchers associated with the Graphene Flagship have reported overcoming the theoretical limiting performance of membranes in gas separation. This collaborative research from CNR, University of Bologna and Graphene-XT has potential applications in hydrogen purification and carbon capture and storage.
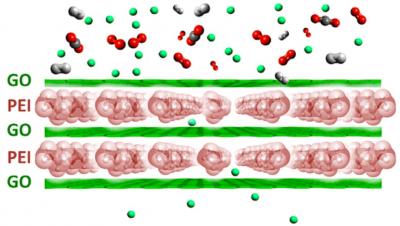
The team explains that polymer-based membranes for gas separation have a trade-off between high gas permeability and high gas selectivity, the so-called Robeson upper bound. By combining individual graphene oxide sheets with polymer spacers, in a sandwich style structure, the researchers have been able to overcome this limit, separating gas quickly and efficiently.
Using a bottom up approach, the researchers deposited alternating layers of graphene oxide and a polymer poly(ethyleneimine) - PEI, using a self assembly method, to make the gas separation membrane. By using graphene oxide, the team was able to deposit individual graphene oxide layers separated by the PEI.
The depth of the PEI layer acting as a spacer between the graphene oxide layers was found to be vitally important to guarantee high gas flux through the membrane. This separation system therefore contains a layered material and an ultra-thin polymer layer with thickness of approximately two nanometers. The graphene oxide sheets make the gaseous molecules to diffuse a path within the PEI chains.
By switching from the standard three-dimensional membrane to a layered polymer structure we achieved gas separation over the Robeson limit in a membrane only 100nm thick, said Professor Vincenzo Palermo, coordinator of the team performing this research and Vice-Director of the Graphene Flagship.
Importantly, it was also found that the permeability of these membranes to different gasses depends strongly on the diameter of the gas molecules. This gives to the membrane a unique selectivity that eventually provides the gas separation technique with both tuneable permeability and high selectivity as well as the potential to be used on the large scale. The increased functionality to the inexpensive PEI films makes these gas separation membranes attractive for various applications.
Through our collaboration with the University of Bologna and Graphene-XT within the Flagship, we have been able to assess the scalable nature of this research in industrial plants to separate gasses, said Palermo.