Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have designed a graphene device that switches from a superconducting material to an insulator and back again to a superconductor â all with a flip of a switch. The team shared that the device exhibits this unique versatility while being thinner than a human hair.
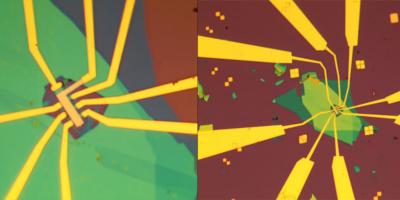 Views of the trilayer graphene/boron nitride heterostructure device as seen through an optical microscope. The gold, nanofabricated electric contacts are shown in yellow; the silicon dioxide/silicon substrate is shown in brown and the boron nitride flakes
Views of the trilayer graphene/boron nitride heterostructure device as seen through an optical microscope. The gold, nanofabricated electric contacts are shown in yellow; the silicon dioxide/silicon substrate is shown in brown and the boron nitride flakes
"Usually, when someone wants to study how electrons interact with each other in a superconducting quantum phase versus an insulating phase, they would need to look at different materials. With our system, you can study both the superconductivity phase and the insulating phase in one place," said Guorui Chen, the study's lead author and a postdoctoral researcher in the lab of Feng Wang, who led the study. Wang, a faculty scientist in Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division, is also a UC Berkeley physics professor.
In a previous study, the researchers reported observing the properties of a Mott insulator in a device made of trilayer graphene. A Mott insulator is a class of material that somehow stops conducting electricity at hundreds of degrees below freezing despite classical theory predicting electrical conductivity. But it has long been believed that a Mott insulator can become superconductive by adding more electrons or positive charges to make it superconductive, Chen explained.
Other researchers have already discovered that moiré superlattices formed with graphene exhibit exotic physics such as superconductivity when the layers are aligned at just the right angle. "So for this study we asked ourselves, 'If our trilayer graphene system is a Mott insulator, could it also be a superconductor?'" said Chen.
Working with David Goldhaber-Gordon of Stanford University and the Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, and Yuanbo Zhang of Fudan University, the researchers used a dilution refrigerator, which can reach intensely cold temperatures of 40 millikelvinsâor nearly minus 460 degrees Fahrenheitâto cool the graphene/boron nitride device down to a temperature at which the researchers expected superconductivity to appear near the Mott insulator phase, said Chen.
Once the device reached a temperature of 4 kelvins (minus 452 degrees Fahrenheit), the researchers applied a range of electrical voltages to the tiny top and bottom gates of the device. As they expected, when they applied a high vertical electrical field to both the top and bottom gates, an electron filled each cell of the graphene/boron nitride device. This caused the electrons to stabilize and stay in place, and this "localization" of electrons turned the device into a Mott insulator.
Then, they applied an even higher electrical voltage to the gates. To their delight, a second reading indicated that the electrons were no longer stable. Instead, they were shuttling around, moving from cell to cell, and conducting electricity without loss or resistance. In other words, the device had switched from the Mott insulator phase to the superconductor phase.
Chen explained that the boron nitride moiré superlattice somehow increases the electron-electron interactions that take place when an electrical voltage is applied to the device, an effect that switches on its superconducting phase. It's also reversibleâwhen a lower electrical voltage is applied to the gates, the device switches back to an insulating state.
The device offers scientists a unique platform for studying the interplay between atoms and electrons in exotic new superconducting materials with potential use in quantum computers - as well as new Mott insulator materials that could one day make tiny 2D Mott transistors for microelectronics a reality.
"This result was very exciting for us. We never imagined that the graphene/boron nitride device would do so well," Chen said. "You can study almost everything with it, from single particles to superconductivity. It's the best system I know of for studying new kinds of physics," Chen said.
This study was supported by the Center for Novel Pathways to Quantum Coherence in Materials (NPQC), an Energy Frontier Research Center led by Berkeley Lab and funded by the DOE Office of Science. NPQC brings together researchers at Berkeley Lab, Argonne National Laboratory, Columbia University, and UC Santa Barbara to study how quantum coherence underlies unexpected phenomena in new materials such as trilayer graphene, with an eye toward future uses in quantum information science and technology.