Graphene composites: introduction and market status
What are composite materials?
Composite materials (also referred to as composition materials, or simply composites) are materials formed by combining two or more materials with different properties to produce an end material with unique characteristics. These materials do not blend or dissolve together but remain distinct within the final composite structure. Composite materials can be made to be stronger, lighter or more durable than traditional materials due to properties they gain from combining their different components.
Most composites are made up of two materials - the matrix (or binder) surrounds a cluster of fibers or fragments of a stronger material (reinforcement). A common example of this structure is fiberglass, which was developed in the 1940’s to be the first modern composite and is still in widespread use. In fiberglass, fine fibers of glass, which are woven into a cloth of sorts, act as the reinforcement in a plastic or resin matrix.
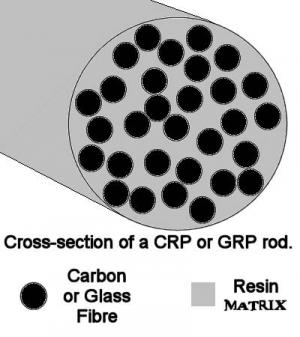
While composite materials are not a new concept (for example, mud bricks, made from dried mud embedded with straw pieces, have been around for thousands of years), recent technologies have brought many new and exciting composites to existence. By careful selection of matrix and reinforcement (as well as the best manufacturing process to bring them together) it is possible to create significantly superior materials, with tailored properties for specific needs. Typical composite materials include composite building materials like cement and concrete, different metal composites, plastic composites and ceramic composites.
How are composite materials made?
The three main factors that help mold the end composite material are the matrix, reinforcement and manufacturing process. As matrix, many composites use resins, which are thermosetting or thermosoftening plastics (hence the name ‘reinforced plastics’ often given to them). These are polymers that hold the reinforcement together and help determine the physical properties of the end composite.
Thermosetting plastics begin as liquid but then harden with heat. They do not return to liquid state and so they are durable, even in extreme exposure to chemicals and wear. Thermosoftening plastics are hard at low temperatures and but soften with heat. They are less commonly used but possess interesting advantages like long shelf life of raw material and capacity for recycling. There are other matrix materials such as ceramics, carbon and metals that are used for specific purposes.
Reinforcement materials grow more varied with time and technology, but the most commonly used ones are still glass fibers. Advanced composites tend to favor carbon fibers as reinforcement, which are much stronger than glass fibers, but are also more expensive. Carbon fiber composites are strong and light, and are used in aircraft structures and sports gear (golf clubs and various rackets). They are also increasingly used to replace metals that replace human bones. Some polymers make good reinforcement materials, and help make composites that are strong and light.
The manufacturing process usually involves a mould, in which the reinforcement is first placed and then the semi-liquid matrix is sprayed or poured in to form the object. Moulding processes are traditionally done by hand, though machine processing is becoming more common. One of the new methods is called ‘pultrusion’ and is ideal for making products that are straight and have a constant cross section, like different kinds of beams. Products that of thin or complex shape (like curved panels) are built up by applying sheets of woven fiber reinforcement, saturated with matrix material, over a mould. Advanced composites (like those which are used in aircraft) are usually made from a honeycomb of plastic held between two sheets of carbon-fiber reinforced composite material, which results in high strength, low weight and bending stiffness.
Where can composites be found?
Composite materials have many obvious advantages, as they can be made to be lightweight, strong, corrosion and heat resistant, flexible, transparent and more according to specific needs. Composites are already used in many industries, like boats, aerospace, sports equipment (golf shafts, tennis rackets, surfboards, hockey sticks and more), Automotive components, wind turbine blades, body armour, building materials, bridges, medical utilities and others. Composite materials’ merits and potential assures ample research in the field which is hoped to bring future developments and implementations in additional markets.

Modern aviation is a specific example of an industry with complex needs and requirements, which benefits greatly from composite materials’ advantages. This industry raises demands of light and strong materials, that are also durable to heat and corrosion. It is no surprise, then, that many aircraft have wing and tail sections, as well as propellers and rotor blades made of composites, along with much of the internal structure.
What is graphene?
Graphene is a two-dimensional matrix of carbon atoms, arranged in a honeycomb lattice. A single square-meter sheet of graphene would weigh just 0.0077 grams but could support up to four kilograms. That means it is thin and lightweight but also incredibly strong. It also has a large surface area, great heat and electricity conductivity and a variety of additional incredible traits. This is probably why scientists and researchers call it “a miracle material†and predict it will revolutionize just about every industry known to man.
Graphene and composite materials
As was stated before, graphene has a myriad of unprecedented attributes, any number of which could potentially be used to make extraordinary composites. The presence of graphene can enhance the conductivity and strength of bulk materials and help create composites with superior qualities. Graphene can also be added to metals, polymers and ceramics to create composites that are conductive and resistant to heat and pressure.
Graphene composites have many potential applications, with much research going on to create unique and innovative materials. The applications seem endless, as one graphene-polymer proves to be light, flexible and an excellent electrical conductor, while another dioxide-graphene composite was found to be of interesting photocatalytic efficiencies, with many other possible coupling of materials to someday make all kinds of composites. The potential of graphene composites includes medical implants, engineering materials for aerospace and renewables and much more.
Further reading
- Graphene Supercapacitors
- Introduction to graphene
- Graphene company database
- How to invest in the graphene revolution
- The Graphene Handbook, our very own guide to the graphene market
Versarien updates on recent progress
Versarien has shared updates on its progress across several key sectors and markets, reporting a growing pipeline of opportunities, rising from £1.6 million (over USD$2 million) in October 2023 to £4.7 million currently (over USD$6,100,000), with £1.6 million (over USD$2 million) in commercial opportunities and £3.1 million (over USD$4 million) in grants. The Company said it continued to focus on developing advanced materials, especially graphene, through manufacturing-light operations and technology licensing.
In the construction sector, the company said it had placed orders for equipment to enhance its in-house construction testing capabilities following a July fundraising. The equipment would support the development of graphene-based products, such as Cementene. Versarien said it had also signed its first significant 3D construction printing (3DCP) contract with Building For Humanity CIC for a project in Accrington, UK. The Company anticipated on-site activities to begin in 2025.
AMD announces collaboration with Xyntra Chemicals
Advanced Material Development (AMD) has entered into a commercial and technical collaboration with Xyntra Chemicals, a prominent player in the supply, manufacture, and development of polymers. The collaboration aims to develop a range of unique customized latex polymers to support AMD’s colorimetric smart sensing technologies. These polymers will be enhanced by graphene, along with additional nanomaterials.
The immediate priority of the new partnership is to optimize Xyntra’s polymer technology to support the early-stage production of AMD's innovative vaccine vial monitor technology and create the production-ready formula that will enable Xyntra to manufacture the solution at scale under license.
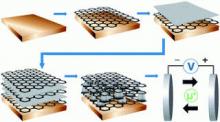
Researchers combine graphene and silk for advanced microelectronics, wearables and next-gen computing applications
While silk protein has been used in designer electronics, its use is currently limited in part because silk fibers are a messy tangle of spaghetti-like strands. To address this, researchers from Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, University of Washington, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, North Carolina State University and Xiamen University have developed a uniform two-dimensional (2D) layer of silk protein fragments, or "fibroins," on graphene.
Scheme of silk fibroin assembly on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) characterized by in situ AFM. Image from Science Advances
The scientists explained that their work provides a reproducible method for silk protein self-assembly that is essential for designing and fabricating silk-based electronics. They said that the system is nontoxic and water-based, which is vital for biocompatibility.
Premier Graphene, HGI Industrial Technologies and Defense Atomics announce strategic partnership for graphene solutions in ballistic protection
Premier Graphene, HGI Industrial Technologies and Defense Atomics have announced a strategic partnership aimed at advancing the production and application of graphene in ballistic protection technologies. This collaboration brings together expertise from the three parties to meet the growing demand for high-performance ballistic solutions.
The partnership focuses on the feasibility studies and testing of hardware developed by Defense Atomics, that integrates advanced graphene solutions for enhanced ballistic protection, ensuring compliance with the security protocols required for classified government contracts.
Mito Materials Solutions and St. Croix Fly announce product line expansion of graphene-enhanced fly fishing rods
Mito Material Solutions has announced a product line expansion by core sporting customer St. Croix Fly. In October 2023, Mito shared how the fly fishing rod company incorporated its functionalized graphene into the composite rods to enable faster recovery, increase torsional rigidity and improve strength-to-weight ratios.
St. Croix’s Technica Series rods were conceived and delivered to give anglers “the upper hand in the trickiest of trout-fishing situations.” Its responsive, moderate action, paired with the use of carbon fiber and Mito’s graphene technology, adds to the line’s speed, endless loop stability and accuracy.
Chang Robotics and Northwestern University’s INVO Lab introduce new graphene-enhanced packaging
Chang Robotics, an engineering company, and Northwestern University’s INVO Lab have announced a joint venture aimed at reducing contamination from microplastics and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the US food supply.
This collaboration has led to the development of GOEco, an initiative that shows that very small amounts of graphene oxide can be infused into paper products or compostable packaging materials to replace plastic and PFAS. GOEco’s primary goal is to replace the widespread use of plastics in food packaging, such as paper plates and disposable utensils. The patent-pending technology helps enhance the environmental friendliness of disposable tableware without compromising functionality.
Black Swan Graphene enters strategic partnership with Broadway Colours
Black Swan Graphene has announced a commercial agreement with Broadway Colours, a UK-based manufacturer of color and additive masterbatches, plastic compounds and rotational molding powders. The Company said the partnership aims to leverage Broadway’s technical expertise, manufacturing capabilities, distribution, and market reach to fast-track the commercialization of Black Swan’s graphene products.
Broadway will use Black Swan’s graphene nanoplatelets to manufacture their Graphene Enhanced Masterbatches (GEMs) targeting a variety of sectors including consumer goods, packaging, automotive, construction, defense, marine and logistics. Its new product range will also feature a bio-based polymer GEM, which Black Swan highlighted offers an eco-friendly alternative to the existing products.
First Graphene joins project that aims to advance low-carbon hydrogen production and storage
First Graphene has announced its partnership in a collaborative project aimed at advancing low-carbon hydrogen production and creating safer, more efficient storage solutions. The Company’s role will involve leveraging its expertise in graphene nanoplatelets to enhance the strength and impermeability of cryogenic hydrogen storage tanks, contributing to a project valued at around $3.72 million.
The project brings together UK and Australian expertise to develop and commercialize novel light-weight impermeable cryogenic all-composite tanks (Type-V) for the safe storage of liquid hydrogen.
Evercloak's HVAC technology gets government funding boost
Canada-based Evercloak's HVAC technology recently received a funding boost, with CAD$1.1 million (over USD$807,000) in funding from Natural Resources Canada's Energy Innovation Program (EIP).
The EIP funding supports a $1.8M project enabling Evercloak to accelerate the development of their membrane-based system, which can cut the energy required for air conditioning and dehumidification by up to 50%. According to the Company's founder and CEO, Evelyn Allen, those reductions will be crucial as global temperatures rise.
Black Swan Graphene launches its fourth commercial Graphene Enhanced Masterbatch product
Black Swan Graphene has announced the release of its fourth commercial Graphene Enhanced Masterbatch ("GEM") product, as it continues to deploy broad commercialization efforts.
This new thermoplastic polyurethane ("TPU") masterbatch is an addition to the GraphCore 01 product line. TPU is a versatile polymer that combines the properties of rubber and plastic, making it an ideal material for a variety of applications ranging from industrial to consumer goods; inflatable products are particularly well suited for this new GEM. Using this new GEM, Black Swan has reportedly demonstrated a 25% improvement in light weighting capability, along with other mechanical performance improvements.
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page



